publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2025
- asoc
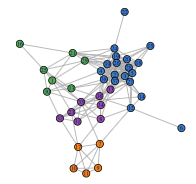 Graph-based analysis of problem space and genetic programming classifier performance using optimal transport dataset distanceJoel Lee Nation, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Yuliana Martínez, Arnoldo Díaz-Ramírez, and Leonardo TrujilloApplied Soft Computing, 2025
Graph-based analysis of problem space and genetic programming classifier performance using optimal transport dataset distanceJoel Lee Nation, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Yuliana Martínez, Arnoldo Díaz-Ramírez, and Leonardo TrujilloApplied Soft Computing, 2025Understanding and interpreting machine learning tasks is a non-trivial endeavor. To this end, many works have proposed creative ways to organize and visualize a problem dataset, the learning process itself, or the models produced after learning has occurred. Moreover, as the scope of machine learning increases, the re-purposing or specialization of models becomes more common, or as continued automation is sought for algorithm deployment, understanding sets of problems has also become relevant. The present work proposes a graph-based representation of a set of machine learning problems, a novel characterization of the relationships and structures that are present in such a set. While similar proposals have been made before, the proposed methodology employs a recent and unique metric between problem datasets, the Optimal Transport Dataset Distance, which allows for the computation of a mathematically rigorous distance matrix for problem sets. This allows for the construction of a graph-based representation, while previous works relied on representations based on problem meta-features that were defined heuristically. Results show that the resulting graph representation of a problem set exhibits structural properties that are related to empirical indicators of problem difficulty, such as the average error, the size of the dataset, and the class imbalance. A similar analysis using meta-features shows that the structure of the resulting graphs cannot capture the same nuanced relationships between problems.
@article{2025_asoc, title = {Graph-based analysis of problem space and genetic programming classifier performance using optimal transport dataset distance}, journal = {Applied Soft Computing}, volume = {184}, pages = {113716}, year = {2025}, issn = {1568--4946}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2025.113716}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494625010270}, author = {Nation, Joel Lee and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Martínez, Yuliana and Díaz-Ramírez, Arnoldo and Trujillo, Leonardo}, keywords = {Genetic programming, Graph-based analysis, Optimal transport dataset distance, Classification}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - sensj
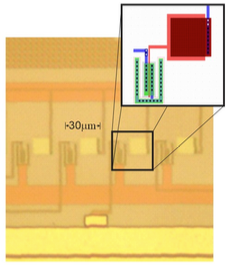 UV Photodetector Based on FG-NMOS in 0.5 μm Standard CMOS TechnologyJesus E. Molinar-Solis, Enrique J. Tinajero-Perez, Ivan Padilla-Cantolla, Juan J. Ocampo-Hidalgo, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Adriana L. Iñiguez Carrillo, Carlos Muñiz-Montero, Jorge Cuevas-Chavez, and Alberto Gudiño-OchoaIEEE Sensors Journal, 2025
UV Photodetector Based on FG-NMOS in 0.5 μm Standard CMOS TechnologyJesus E. Molinar-Solis, Enrique J. Tinajero-Perez, Ivan Padilla-Cantolla, Juan J. Ocampo-Hidalgo, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Adriana L. Iñiguez Carrillo, Carlos Muñiz-Montero, Jorge Cuevas-Chavez, and Alberto Gudiño-OchoaIEEE Sensors Journal, 2025@article{2025_sensj, author = {Molinar-Solis, Jesus E. and Tinajero-Perez, Enrique J. and Padilla-Cantolla, Ivan and Ocampo-Hidalgo, Juan J. and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Iñiguez Carrillo, Adriana L. and Muñiz-Montero, Carlos and Cuevas-Chavez, Jorge and Gudiño-Ochoa, Alberto}, journal = {IEEE Sensors Journal}, title = {UV Photodetector Based on FG-NMOS in 0.5 μm Standard CMOS Technology}, year = {2025}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1-1}, keywords = {CMOS technology;Detectors;Sensors;Photodetectors;Silicon;MOSFET;Transconductance;Sensor arrays;Electric potential;Standards;ultraviolet photodetectors;silicon-based UV detectors;CMOS photodetectors}, doi = {10.1109/JSEN.2025.3586820}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - applsci
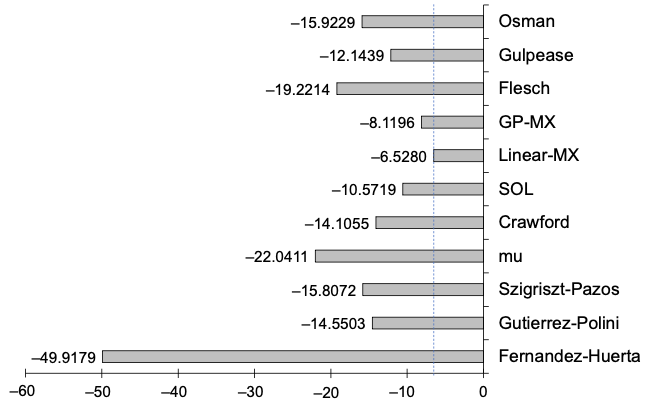 Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican SpanishDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Lino Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Miguel Ángel Álvarez-Carmona, and Ansel Y. Rodríguez-GonzálezApplied Sciences, 2025
Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican SpanishDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Lino Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Miguel Ángel Álvarez-Carmona, and Ansel Y. Rodríguez-GonzálezApplied Sciences, 2025Readability formulas are mathematical functions that assess the ‘difficulty’ level of a given text. They play a crucial role in aligning educational texts with student reading abilities; however, existing models are often not tailored to specific linguistic or regional contexts. This study aims to develop and evaluate two novel readability formulas specifically designed for the Mexican Spanish language, targeting elementary education levels. The formulas were trained on a corpus of 540 texts drawn from official elementary-level textbooks issued by the Mexican public education system. The first formula was constructed using multiple linear regression, emulating the structure of traditional readability models. The second was derived through genetic programming (GP), a machine learning technique that evolves symbolic expressions based on training data. Both approaches prioritize interpretability and use standard textual features, such as sentence length, word length, and lexical and syntactic complexity. Experimental results show that the proposed formulas outperform several well-established Spanish and non-Spanish readability formulas in distinguishing between grade levels, particularly for early and intermediate stages of elementary education. The GP-based formula achieved the highest alignment with target grade levels while maintaining a clear analytical form. These findings underscore the potential of combining machine learning with interpretable modeling techniques and highlight the importance of linguistic and curricular adaptation in readability assessment tools.
@article{2025_applsci, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, Lino and Sánchez-Cervantes, María Guadalupe and Álvarez-Carmona, Miguel Ángel and Rodríguez-González, Ansel Y.}, title = {Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican Spanish}, journal = {Applied Sciences}, volume = {15}, year = {2025}, number = {13}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/15/13/7259}, issn = {2076--3417}, doi = {10.3390/app15137259}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - tevc
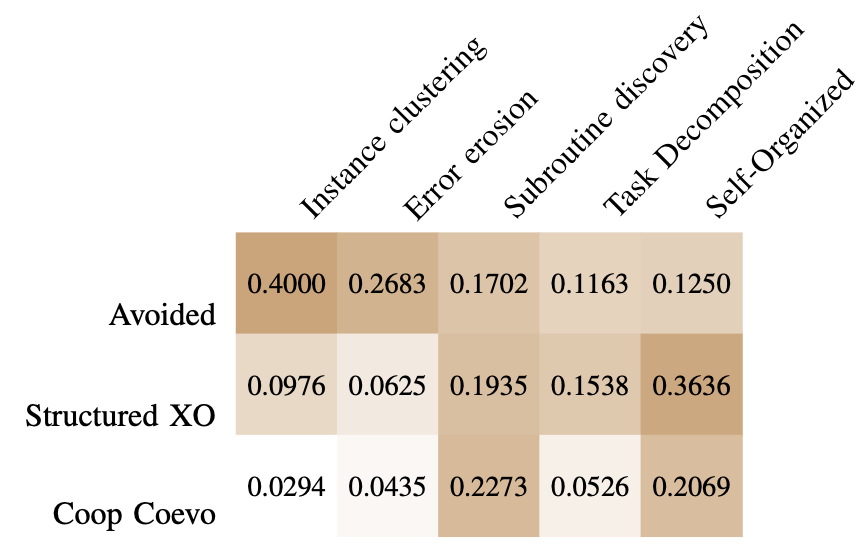 Problem Decomposition Strategies and Credit Distribution Mechanisms in Modular Genetic Programming for Supervised LearningLino Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Maria Guadalupe Sánchez CervantesIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025
Problem Decomposition Strategies and Credit Distribution Mechanisms in Modular Genetic Programming for Supervised LearningLino Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Maria Guadalupe Sánchez CervantesIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025In this review article, we provide a comprehensive guide to the endeavor of problem decomposition within the field of Genetic Programming (GP), specifically tree-based GP for supervised learning tasks. We analyzed in detail 70 manuscripts that deal with motifs such as “problem decomposition”“, modular GP”“, subroutine evolution”“, hierarchical GP”“, cooperative coevolution”, among others. As a result of this study, we propose an unifying taxonomy that categorizes efforts on problem decomposition in GP along three major axes: the architecture of evolved composite solutions, problem decomposition strategy, and credit assignment approach. This classification system sheds light on how the diverse proposed methodologies for problem decomposition relate to each other and where most of the research efforts have focused to this day. Rather than discussing in detail any particular set of works, we see this overview as a map that may help researchers in obtaining a wider view of existing efforts for problem decomposition in GP, as well as provide a cohesive framework that allows the disclosure of future developments in clearly differentiated niches. We close the article with a brief analysis that compares the current state of problem decomposition methodologies in GP with that of another exemplar of problem decomposition in machine learning: deep learning.
@article{2025_tevc, author = {Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, Lino and Rodríguez-González, Ansel Y. and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Cervantes, Maria Guadalupe Sánchez}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation}, title = {Problem Decomposition Strategies and Credit Distribution Mechanisms in Modular Genetic Programming for Supervised Learning}, year = {2025}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1--1}, keywords = {Algorithms;Reviews;Evolutionary computation;Supervised learning;Taxonomy;Genetic programming;Estimation;Deep learning;Syntactics;Random forests;Genetic Programming;problem decomposition;Machine Learning;Cooperative Coevolution;Deep Learning;modularity;ADF}, doi = {10.1109/TEVC.2025.3526581}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - riiit
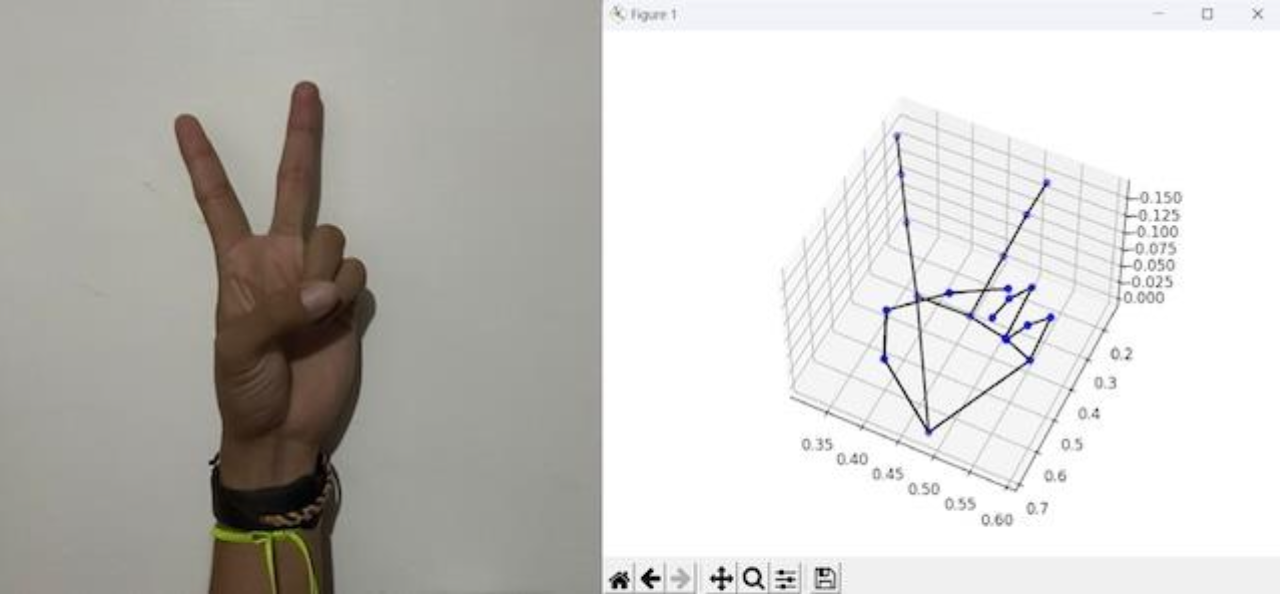 Desarrollo de un sistema automático de reconocimiento de la LSM para dispositivos móvilesJosé Luis Mendoza-Tene, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Silvia Berenice Fajardo-Flores, and María Eugenia Puga-NathalRevista Internacional de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica, 2025
Desarrollo de un sistema automático de reconocimiento de la LSM para dispositivos móvilesJosé Luis Mendoza-Tene, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Silvia Berenice Fajardo-Flores, and María Eugenia Puga-NathalRevista Internacional de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica, 2025En este artículo se estudia la efectividad de utilizar dispositivos móviles para el reconocimiento automático de señas estáticas y dinámicas de la lengua de señas mexicana (LSM). Esto debido a que la mayoría de los trabajos actuales para el reconocimiento de la LSM, generalmente se centran en un tipo de seña (estática o dinámica) y casi siempre consideran dispositivos especializados fuera del alcance de la población. Para llevar a cabo este estudio, se implementó una solución que consta de una aplicación Android para capturar vídeos y enviarlos a un servicio Web en la nube, donde se aloja un sistema de reconocimiento automático. El sistema utiliza el algoritmo de deformación dinámica del tiempo (DTW, por sus siglas en inglés) para comparar las características del vídeo recibido con las de un conjunto de vídeos catalogados por seña. Cabe resaltar que este trabajo sería el primero en utilizar el DTW para señas estáticas de la LSM. Finalmente, se llevó a cabo un estudio experimental del desempeño del sistema utilizando tres dispositivos móviles de diferentes capacidades tanto para la captura del vídeo como en el procesamiento. Los resultados indican que, aunque la calidad de la cámara afecta la eficiencia del reconocimiento, esta no es determinante; además, debido al método de caracterización de los vídeos y por atributos propios de la LSM, el sistema tiende a reconocer mejor las señas estáticas que las dinámicas, incluso con el uso del DTW.
@article{2025_riiit, author = {Mendoza-Tene, José Luis and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Fajardo-Flores, Silvia Berenice and Puga-Nathal, María Eugenia}, journal = {Revista Internacional de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica}, title = {Desarrollo de un sistema automático de reconocimiento de la LSM para dispositivos móviles}, year = {2025}, volume = {12}, number = {72}, pages = {1--22}, keywords = {Mexican sign language, Automatic recognition system, Dynamic time warping, Mobile app}, url = {https://riiit.com.mx/apps/site/files_v2450/lsm_jal_1_riiit_ene-feb_2025.pdf}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2024
- simpa
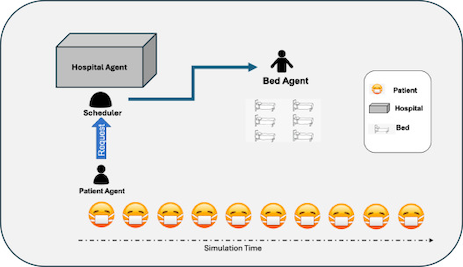 MaSchedule. A multi-agent tool for scheduling problemsJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Candelaria E. Sansores, Francisco J. Hernandez-Lopez, Jonás Velasco, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Jose Luis Lopez-Martinez, and Julio Cesar Ramirez-PachecoSoftware Impacts, 2024
MaSchedule. A multi-agent tool for scheduling problemsJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Candelaria E. Sansores, Francisco J. Hernandez-Lopez, Jonás Velasco, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Jose Luis Lopez-Martinez, and Julio Cesar Ramirez-PachecoSoftware Impacts, 2024Several scheduling optimization problems belong to the NP-complete class, including, task scheduling, job shop scheduling, and patient admission. These problems commonly require the development of heuristics approaches to find near-optimal solutions within reasonable timeframes. In this work, we present MaSchedule an open-source multi-agent tool for the design of heuristics for scheduling problems.
@article{2024_simpa, title = {MaSchedule. A multi-agent tool for scheduling problems}, journal = {Software Impacts}, pages = {100726}, year = {2024}, issn = {2665-9638}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpa.2024.100726}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665963824001143}, author = {Trejo-Sánchez, Joel Antonio and Sansores, Candelaria E. and Hernandez-Lopez, Francisco J. and Velasco, Jonás and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Lopez-Martinez, Jose Luis and Ramirez-Pacheco, Julio Cesar}, keywords = {Multi-agent system, Simulation, Scheduling}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ingeniantes
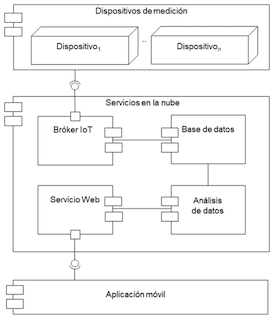 Arquitectura Cloud-IoT para el monitoreo de la calidad del aire en interioresOrlando Valentín Javier-Silva, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Ramón Chávez-Bracamontes, Raúl Rentería-Toriz, Fernando Mancilla Peña, and María Guadalupe Sánchez-CervantesIngeniantes, 2024
Arquitectura Cloud-IoT para el monitoreo de la calidad del aire en interioresOrlando Valentín Javier-Silva, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Ramón Chávez-Bracamontes, Raúl Rentería-Toriz, Fernando Mancilla Peña, and María Guadalupe Sánchez-CervantesIngeniantes, 2024Currently, attention towards Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) has become important given its direct impact on people’s health and well-being. In response to this growing concern, this article presents a Cloud-IoT architecture that fuses Internet of Things and cloud computing technologies for functional IAQ monitoring. This architecture integrates devices equipped with sensors of environmental variables (temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds) that together allow the IAQ to be evaluated. Additionally, the architecture implements cloud services for secure and scalable processing/storage of the data generated by the devices. Likewise, the architecture includes a mobile application that allows users to manage one or more devices and access cloud services. The application also allows users to view the IAQ in current time or through historical data from their devices.
@article{2024_ingeniantes, title = {Arquitectura Cloud-IoT para el monitoreo de la calidad del aire en interiores}, journal = {Ingeniantes}, volume = {3}, number = {1}, pages = {28--33}, year = {2024}, issn = {2395-9452}, url = {https://citt.itsm.edu.mx/ingeniantes/pdfversion/ingeniantes11no1vol3-esp.pdf}, author = {Javier-Silva, Orlando Valentín and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Chávez-Bracamontes, Ramón and Rentería-Toriz, Raúl and Mancilla Peña, Fernando and Sánchez-Cervantes, María Guadalupe}, keywords = {Cloud-IoT, Cloud Computing, Indoor Air Quality, Internet of Things, Mobile App}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - comspeech
 Addressing subjectivity in paralinguistic data labeling for improved classification performance: A case study with Spanish-speaking Mexican children using data balancing and semi-supervised learningDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Isabel G. Vázquez-Gómez, and Humberto Pérez-EspinosaComputer Speech & Language, 2024
Addressing subjectivity in paralinguistic data labeling for improved classification performance: A case study with Spanish-speaking Mexican children using data balancing and semi-supervised learningDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Isabel G. Vázquez-Gómez, and Humberto Pérez-EspinosaComputer Speech & Language, 2024Paralinguistics is an essential component of verbal communication, comprising elements that provide additional information to the language, such as emotional signals. However, the subjective nature of perceiving affective aspects, such as emotions, poses a significant challenge to the development of quality resources for training recognition models of paralinguistic features. Labelers may have different opinions and perceive different emotions from others, making it difficult to achieve a diverse and sufficient representation of considered categories. In this study, we focused on the automatic classification of paralinguistic aspects in Spanish-speaking Mexican children of elementary school age. However, the dataset presents a strong imbalance in all labeled aspects and a low agreement between the labelers. Furthermore, the audio samples were too short, making it challenging to accurately classify affective speech. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method that combines data balancing algorithms and semisupervised learning to improve the classification performance of the trained models. Our method aims to mitigate the subjectivity involved in labeling paralinguistic data, thus advancing the development of robust and accurate recognition models of affective aspects in speech.
@article{2024_comspec, title = {Addressing subjectivity in paralinguistic data labeling for improved classification performance: A case study with Spanish-speaking Mexican children using data balancing and semi-supervised learning}, journal = {Computer Speech & Language}, pages = {101652}, year = {2024}, issn = {0885-2308}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2024.101652}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0885230824000354}, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Vázquez-Gómez, Isabel G. and Pérez-Espinosa, Humberto}, keywords = {Computational paralinguistics, Paralinguistic information, Semi-supervised learning, Subjective emotional analysis}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ApplSci
 Genetic Programming to Remove Impulse Noise in Color ImagesDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González, Sergio Sandoval-Pérez, Jesús Ezequiel Molinar-Solís, and María Guadalupe Sánchez-CervantesApplied Sciences, 2024
Genetic Programming to Remove Impulse Noise in Color ImagesDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González, Sergio Sandoval-Pérez, Jesús Ezequiel Molinar-Solís, and María Guadalupe Sánchez-CervantesApplied Sciences, 2024This paper presents a new filter to remove impulse noise in digital color images. The filter is adaptive in the sense that it uses a detection stage to only correct noisy pixels. Detecting noisy pixels is performed by a binary classification model generated via genetic programming, a paradigm of evolutionary computing based on natural biological selection. The classification model training considers three impulse noise models in color images: salt and pepper, uniform, and correlated. This is the first filter generated by genetic programming exploiting the correlation among the color image channels. The correction stage consists of a vector median filter version that modifies color channel values if some are noisy. An experimental study was performed to compare the proposed filter with others in the state-of-the-art related to color image denoising. Their performance was measured objectively through the image quality metrics PSNR, MAE, SSIM, and FSIM. Experimental findings reveal substantial variability among filters based on noise model and image characteristics. The findings also indicate that, on average, the proposed filter consistently exhibited top-tier performance values for the three impulse noise models, surpassed only by a filter employing a deep learning-based approach. Unlike deep learning filters, which are black boxes with internal workings invisible to the user, the proposed filter has a high interpretability with a performance close to an equilibrium point for all images and noise models used in the experiment.
@article{2024_applsci, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Rodríguez-González, Ansel Y. and Sandoval-Pérez, Sergio and Molinar-Solís, Jesús Ezequiel and Sánchez-Cervantes, María Guadalupe}, title = {Genetic Programming to Remove Impulse Noise in Color Images}, journal = {Applied Sciences}, volume = {14}, year = {2024}, number = {1}, article-number = {126}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/14/1/126}, issn = {2076-3417}, doi = {10.3390/app14010126}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2023
- jcsc
 Electrical Characterization of the Clamping Behavior on CMOS Quasi-Floating-Gate CircuitsJesus E. Molinar-Solis, Daniel Sanchez-Arias, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Juan J. Ocampo-Hidalgo, and Ivan Padilla-CantoyaJournal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 2023
Electrical Characterization of the Clamping Behavior on CMOS Quasi-Floating-Gate CircuitsJesus E. Molinar-Solis, Daniel Sanchez-Arias, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Juan J. Ocampo-Hidalgo, and Ivan Padilla-CantoyaJournal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 2023In this paper, the clamping effect introduced by several diode-based configurations used for the implementation of the high-value resistors in quasi-floating-gate circuits is analyzed and characterized. In contrast to previous approaches where a parasitic diode is treated as a simple high-value resistor reducing the circuit complexity, in this case the analysis considers the diode behavior which leads to a clamping circuit. This clamping circuit introduces an unwanted amplitude-dependent offset voltage, which affects the performance moving the quiescent point at the quasi-floating-gate transistors. A new anti-parallel diode configuration for quasi-floating-gate applications is proposed in this work, which eliminates this unwanted offset voltage. The proposed design is validated using simulations and experimental data in a CMOS 0.35-μm technology.
@article{2023_jcsc, author = {Molinar-Solis, Jesus E. and Sanchez-Arias, Daniel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Ocampo-Hidalgo, Juan J. and Padilla-Cantoya, Ivan}, title = {Electrical Characterization of the Clamping Behavior on CMOS Quasi-Floating-Gate Circuits}, journal = {Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers}, volume = {0}, number = {0}, pages = {2450068}, year = {2023}, isbn = {0218-1266}, doi = {10.1142/S0218126624500683}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126624500683}, eprint = {https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126624500683}, publisher = {World Scientific Publishing Co.}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - jpdc
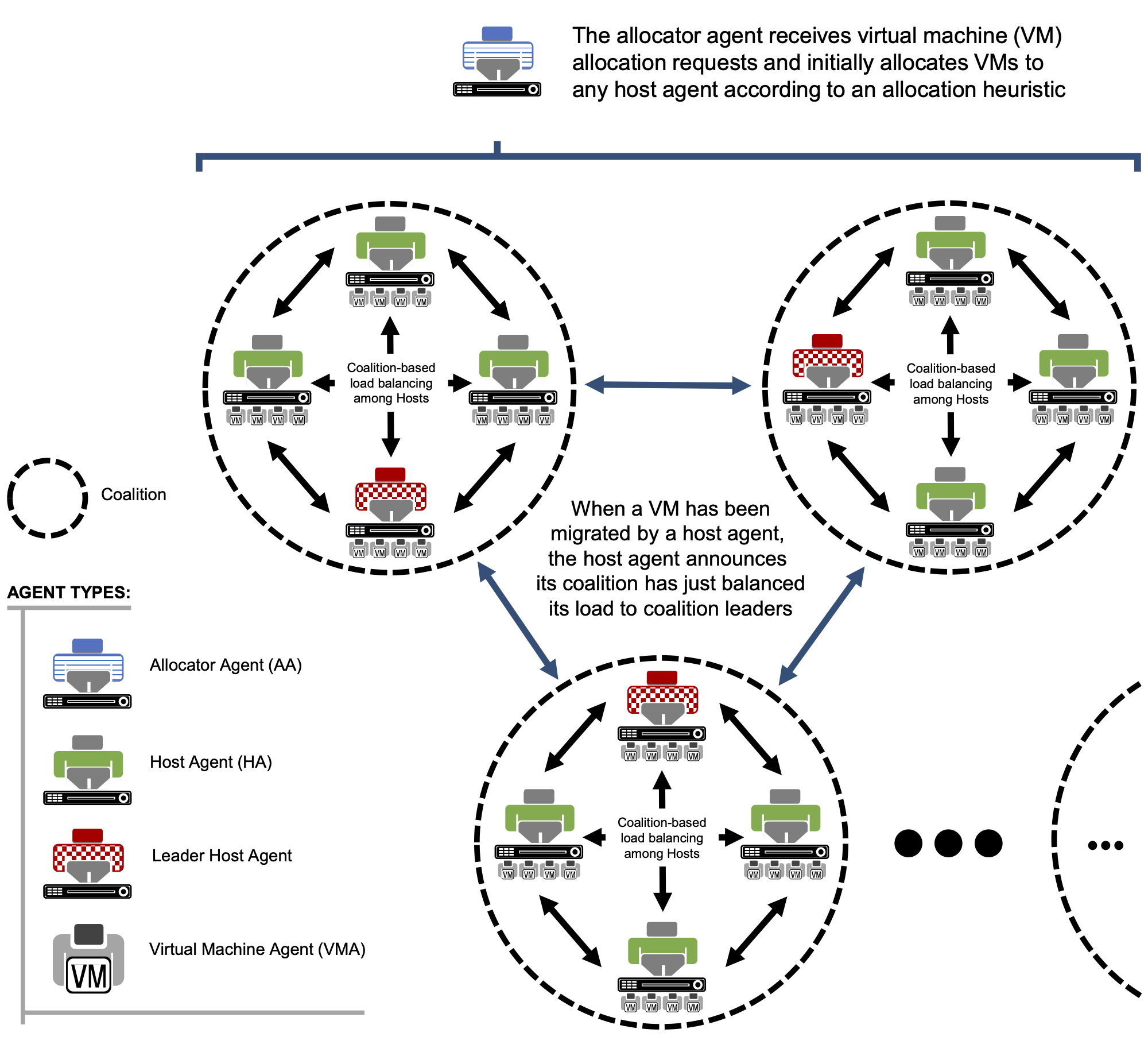 Agent coalitions for load balancing in cloud data centersJ. Octavio Gutierrez-Garcia, Joel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoJournal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2023
Agent coalitions for load balancing in cloud data centersJ. Octavio Gutierrez-Garcia, Joel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoJournal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2023The workload of Cloud data centers is constantly fluctuating causing imbalances across physical hosts that may lead to violations of service-level agreements. To mitigate workload imbalances, this work proposes a concurrent agent-based problem-solving technique supported by cooperative game theory capable of balancing workloads by means of live migration of virtual machines (VMs). Nearby agents managing physical hosts are partitioned into coalitions in which agents play coalitional games to progressively balance separate sections of a data center while considering the coalition’s benefit of migrating a VM as well as its associated network overhead. Simulation results show that, in general, the proposed coalition-based load balancing mechanism outperformed a load balancing mechanism based on a hill-climbing algorithm used by a top data center vendor when considering altogether (i) the standard deviation of resource usage, (ii) the number of migrations, and (iii) the number of switch hops per migration.
@article{2023_jpdc, title = {Agent coalitions for load balancing in cloud data centers}, journal = {Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing}, volume = {172}, pages = {1-17}, year = {2023}, issn = {0743-7315}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2022.10.006}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0743731522002143}, author = {Gutierrez-Garcia, J. Octavio and Trejo-Sánchez, Joel Antonio and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, keywords = {Load balancing, Cloud data centers, Cloud computing, Intelligent agents, Cooperative game theory}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2022
- KingSaud
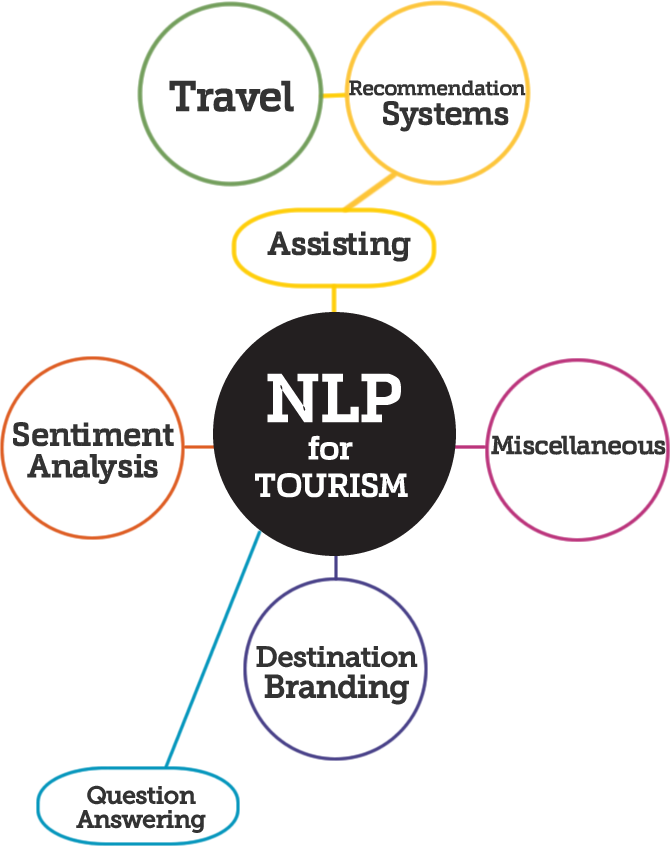 Natural language processing applied to tourism research: A systematic review and future research directionsMiguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, Ramón Aranda, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-Gonzalez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Humberto Pérez-Espinosa, Juan Martínez-Miranda, Rafael Guerrero-Rodríguez, Lázaro Bustio-Martínez, and Ángel Díaz-PachecoJournal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 2022
Natural language processing applied to tourism research: A systematic review and future research directionsMiguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, Ramón Aranda, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-Gonzalez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Humberto Pérez-Espinosa, Juan Martínez-Miranda, Rafael Guerrero-Rodríguez, Lázaro Bustio-Martínez, and Ángel Díaz-PachecoJournal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 2022The social networks and the rapid development of new technologies have led to considerable changes in the tourism industry. Artificial intelligence, in particular natural language processing (NLP), presupposes a significant advantage in obtaining information on the mass content generated by online users concerning tourism services and products. This work presents a systematic review of the use of NLP in the tourism industry and research. We used the well-known PRISMA methodology, and 227 relevant studies over the last decade have been reviewed. Our analysis identified the main methodologies, tools, data sources, and other relevant features in the field. One of the principal contributions of this study is a taxonomy for using NLP in tourism. In addition, metadata were examined using a threefold approach: (i) general statistics, (ii) abstract text analysis, and (iii) keyword networks. Automatic analyses have identified six major topics in applying NLP to tourism issues and have shown that China, the United States, Thailand, and Spain share similar tourism issues or approaches.
@article{2022_king_saud, title = {Natural language processing applied to tourism research: A systematic review and future research directions}, journal = {Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences}, year = {2022}, issn = {1319-1578}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.10.010}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319157822003615}, author = {Álvarez-Carmona, Miguel Á. and Aranda, Ramón and Rodríguez-Gonzalez, Ansel Y. and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Sánchez, María Guadalupe and Pérez-Espinosa, Humberto and Martínez-Miranda, Juan and Guerrero-Rodríguez, Rafael and Bustio-Martínez, Lázaro and Díaz-Pacheco, Ángel}, keywords = {Tourism, Natural language processing, Systematic review}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - sepln
 Overview of Rest-Mex at IberLEF 2022: Recommendation System, Sentiment Analysis and Covid Semaphore Prediction for Mexican Tourist TextsMiguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, Ángel Díaz-Pacheco, Ramón Aranda, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Rafael Guerrero-Rodríguez, and Lázaro Bustio-MartínezProcesamiento del Lenguaje Natural, 2022
Overview of Rest-Mex at IberLEF 2022: Recommendation System, Sentiment Analysis and Covid Semaphore Prediction for Mexican Tourist TextsMiguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, Ángel Díaz-Pacheco, Ramón Aranda, Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Rafael Guerrero-Rodríguez, and Lázaro Bustio-MartínezProcesamiento del Lenguaje Natural, 2022This paper presents the framework and results from the Rest-Mex task at IberLEF 2022. This task considered three tracks: Recommendation System, Sentiment Analysis and Covid Semaphore Prediction, using texts from Mexican touristic places. The Recommendation System task consists in predicting the degree of satisfaction that a tourist may have when recommending a destination of Nayarit, Mexico, based on places visited by the tourists and their opinions. On the other hand, the Sentiment Analysis task predicts the polarity of an opinion issued and the attraction by a tourist who traveled to the most representative places in Mexico. We have built corpora for both tasks considering Spanish opinions from the TripAdvisor website. As a novelty, the Covid Semaphore Prediction task aims to predict the color of the Mexican Semaphore for each state, according to the Covid news in the state, using data from the Mexican Ministry of Health. This paper compares and discusses the participants’ results for all three tacks.
@article{2022_sepln, author = {\'Alvarez-Carmona, Miguel \'A. and Díaz-Pacheco, \'Angel and Aranda, Ram\'on and Rodr\'iguez-Gonz\'alez, Ansel Y. and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Guerrero-Rodr\'iguez, Rafael and Bustio-Mart\'inez, L\'azaro}, title = {Overview of Rest-Mex at IberLEF 2022: Recommendation System, Sentiment Analysis and Covid Semaphore Prediction for Mexican Tourist Texts}, journal = {Procesamiento del Lenguaje Natural}, volume = {69}, number = {0}, year = {2022}, issn = {1989-7553}, url = {http://journal.sepln.org/sepln/ojs/ojs/index.php/pln/article/view/6449}, pages = {289--299}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ipdps
 Teaching High-Performance Computing in Developing Countries: A Case Study in Mexican UniversitiesJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Francisco Javier Hernández-López, Miguel ángel Uh Zapata, José Luis López-Martínez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Julio César Ramírez-PachecoIn 2022 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW) , 2022
Teaching High-Performance Computing in Developing Countries: A Case Study in Mexican UniversitiesJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Francisco Javier Hernández-López, Miguel ángel Uh Zapata, José Luis López-Martínez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Julio César Ramírez-PachecoIn 2022 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW) , 2022@inproceedings{2022_ipdps, author = {Trejo-S\'anchez, Joel Antonio and Hern\'andez-L\'opez, Francisco Javier and Uh Zapata, Miguel \'angel and L\'opez-Mart\'inez, Jos\'e Luis and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Ram\'irez-Pacheco, Julio C\'esar}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW)}, title = {Teaching High-Performance Computing in Developing Countries: A Case Study in Mexican Universities}, year = {2022}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {338-345}, doi = {10.1109/IPDPSW55747.2022.00066}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ApplSci
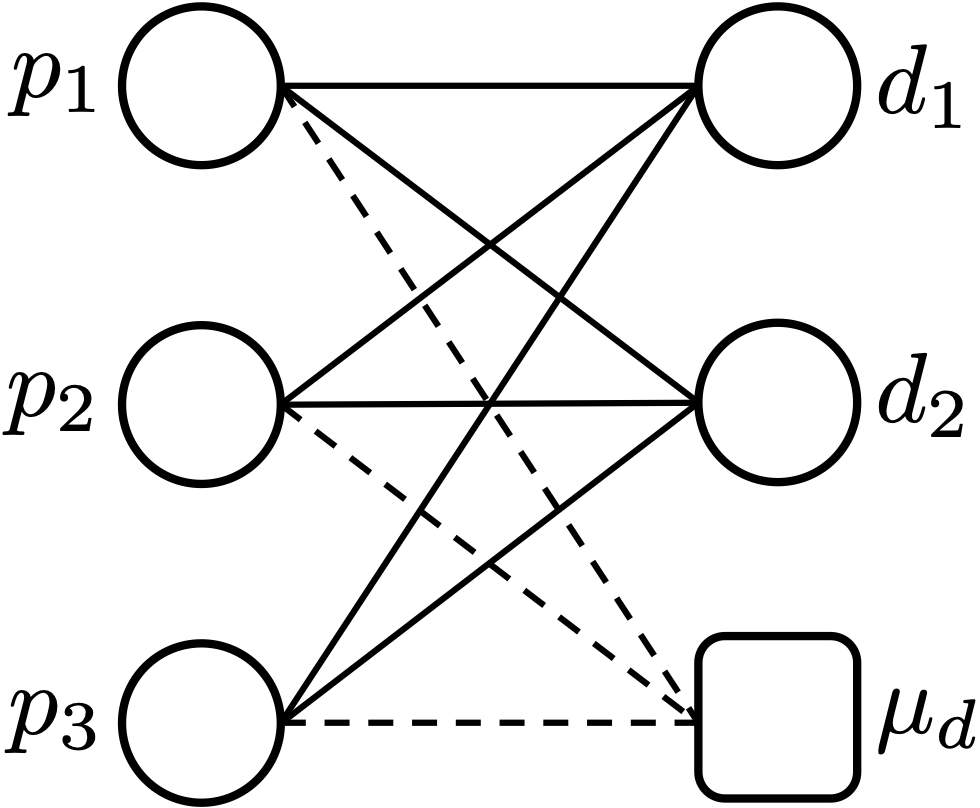 Stable Matching of Users in a Ridesharing ModelDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Carlos Hernández-Bernal, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Joel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Ismael Edrein Espinosa-Curiel, and Jesús Ezequiel Molinar-SolisApplied Sciences, 2022
Stable Matching of Users in a Ridesharing ModelDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, Carlos Hernández-Bernal, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Joel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Ismael Edrein Espinosa-Curiel, and Jesús Ezequiel Molinar-SolisApplied Sciences, 2022A ridesharing system is a transport mode where two or more users share the same vehicle and divide the trip’s expenses based on similar routes and itineraries. Popular ridesharing systems, such as Uber, Flinc, and Lyft, define a matching among users based only on the coincidence of routes. However, these systems do not guarantee a stable matching (i.e., a matching in which no user prefers another different from the assigned one). In this work, a new ridesharing system model is proposed, including three types of trips: identical, inclusive, and partial. This model is used to introduce a new algorithm to address the stable matching problem for ridesharing systems. Finally, a set of experimental simulations of the proposed algorithm is conducted. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm always produces a stable matching.
@article{2022_applsci, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Hern\'andez-Bernal, Carlos and S\'anchez-Cervantes, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Trejo-S\'anchez, Joel Antonio and Espinosa-Curiel, Ismael Edrein and Molinar-Solis, Jes\'us Ezequiel}, title = {Stable Matching of Users in a Ridesharing Model}, journal = {Applied Sciences}, volume = {12}, year = {2022}, number = {15}, article-number = {7797}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/15/7797}, issn = {2076-3417}, doi = {10.3390/app12157797}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2021
- micai
 A Tourist Recommendation System: A Study Case in MexicoSamuel Arce-Cardenas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Miguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, and Juan Pablo Ramírez-SilvaIn Advances in Soft Computing , 2021
A Tourist Recommendation System: A Study Case in MexicoSamuel Arce-Cardenas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Miguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, and Juan Pablo Ramírez-SilvaIn Advances in Soft Computing , 2021The present work deals with implementing tourist recommendation systems designed to predict the user preferences about a place or tourist activity in Mexico. Three recommendation systems have been proposed: two based on collaborative filtering (user and items) and the other based on demographic issues. To this aim, a corpus has been built by collecting 2,263 ratings from TripAdvisor.com about eighteen tourist places in Mexico. Experimental results show that the demographic-based recommendation system outperforms those based on collaborative filtering, obtaining a mean absolute error of 0.67 and a mean square error of 1.2980. These results also show significant improvement over a majority class baseline based on a sizeable unbalanced corpus.
@inproceedings{2021_micai, author = {Arce-Cardenas, Samuel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and \'Alvarez-Carmona, Miguel \'A. and Ram\'irez-Silva, Juan Pablo}, editor = {Batyrshin, Ildar and Gelbukh, Alexander and Sidorov, Grigori}, title = {A Tourist Recommendation System: A Study Case in Mexico}, booktitle = {Advances in Soft Computing}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {184--195}, isbn = {978-3-030-89820-5}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-89820-5\_15}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - sepln
 Overview of Rest-Mex at IberLEF 2021: Recommendation System for Text Mexican TourismMiguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, Ramón Aranda, Samuel Arce-Cardenas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Rafael Guerrero-Rodríguez, A. Pastor López-Monroy, Juan Martínez-Miranda, Humberto Pérez-Espinosa, and Ansel Y. Rodríguez-GonzálezProcesamiento del Lenguaje Natural, 2021
Overview of Rest-Mex at IberLEF 2021: Recommendation System for Text Mexican TourismMiguel Á. Álvarez-Carmona, Ramón Aranda, Samuel Arce-Cardenas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Rafael Guerrero-Rodríguez, A. Pastor López-Monroy, Juan Martínez-Miranda, Humberto Pérez-Espinosa, and Ansel Y. Rodríguez-GonzálezProcesamiento del Lenguaje Natural, 2021This paper presents the framework and results from the Rest-Mex track at IberLEF 2021. This track considered two tasks: Recommendation System and Sentiment Analysis, using texts from Mexican touristic places. The Recommendation System task consists in predicting the degree of satisfaction that a tourist may have when recommending a destination of Nayarit, Mexico, based on places visited by the tourists and their opinions. On the other hand, the Sentiment Analysis task predicts the polarity of an opinion issued by a tourist who traveled to the most representative places in Guanajuato, Mexico. For both tasks, we have built new corpora considering Spanish opinions from the TripAdvisor website. This paper compares and discusses the results of the participants for both tasks.
@article{2021_sepln, author = {\'Alvarez-Carmona, Miguel \'A. and Aranda, Ram\'on and Arce-Cardenas, Samuel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Guerrero-Rodríguez, Rafael and L\'opez-Monroy, A. Pastor and Mart\'inez-Miranda, Juan and P\'erez-Espinosa, Humberto and Rodr\'iguez-Gonz\'alez, Ansel Y.}, title = {Overview of Rest-Mex at IberLEF 2021: Recommendation System for Text Mexican Tourism}, journal = {Procesamiento del Lenguaje Natural}, volume = {67}, number = {0}, year = {2021}, keywords = {Rest-Mex 2021, Recommendation System, Sentiment Analysis, Mexican Tourist Text}, issn = {1989-7553}, url = {http://journal.sepln.org/sepln/ojs/ojs/index.php/pln/article/view/6386}, pages = {163--172}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - difu100cia
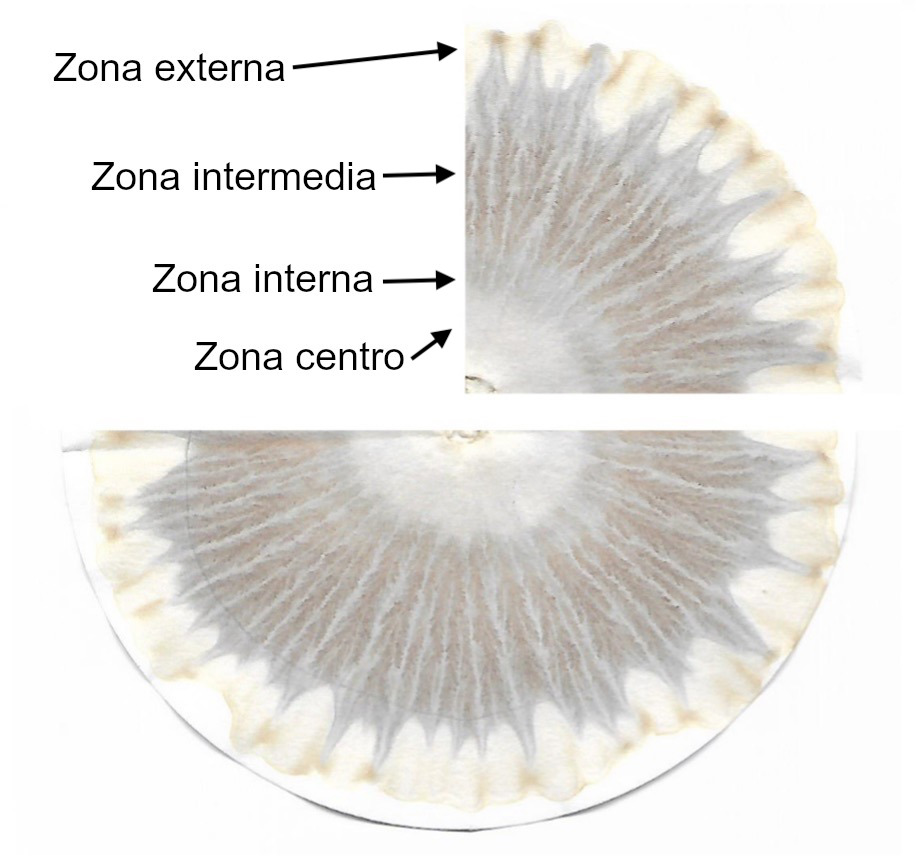 Uso del aprendizaje máquina para el análisis de suelosLuis Enrique Partida-Aguilar, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Raquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Himer Ávila-George, and Jesús Ezequiel Molinar-SolisDifu100ci@, Revista de difusión científica, ingeniería y tecnologías, 2021
Uso del aprendizaje máquina para el análisis de suelosLuis Enrique Partida-Aguilar, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Raquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Himer Ávila-George, and Jesús Ezequiel Molinar-SolisDifu100ci@, Revista de difusión científica, ingeniería y tecnologías, 2021La cromatografía circular de Pfeiffer (PCC, por sus siglas en inglés) es una técnica de análisis cualitativa que provee de información microbiológica, mineral y de materia orgánica del estado de salud de un suelo. El presente trabajo trata de la conformación de un conjunto de datos de imágenes PCC de diferentes tipos de suelos con base en tres variables: acidez, conductividad eléctrica y textura del suelo. Este trabajo también explora el uso de técnicas de aprendizaje profundo para extraer automáticamente las características de las imágenes y clasificar los suelos con base en su tipo. Es la primera vez que se utilizan este tipo de técnicas de aprendizaje para este problema de clasificación. Los resultados experimentales muestran un puntaje-F1 de 0.7889 para la clasificación de la textura de los suelos, lo que sugiere una relación significativa de esta variable con el PCC. Por otra parte, los resultados también sugieren una baja correlación de los PCC con las variables de acidez y conductividad eléctrica de los suelos.
@article{2021_difu100cia_1, author = {Partida-Aguilar, Luis Enrique and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Ochoa-Ornelas, Raquel and \'Avila-George, Himer and Molinar-Solis, Jes\'us Ezequiel}, title = {Uso del aprendizaje m\'aquina para el an\'alisis de suelos}, journal = {Difu100ci@, Revista de difusi\'on cient\'ifica, ingenier\'ia y tecnolog\'ias}, year = {2021}, volume = {15}, number = {3}, pages = {116-123}, url = {http://difu100cia.uaz.edu.mx/index.php/difuciencia/article/view/218}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - difu100cia
 Interpolación de datos ópticos discontinuos mediante series de Fourier y Método Whittaker: un toolbox escrito en pythonHumberto Cruz-Sanabria, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Santiago Belda, Juan Pablo Rivera-Caicedo, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoDifu100ci@, Revista de difusión científica, ingeniería y tecnologías, 2021
Interpolación de datos ópticos discontinuos mediante series de Fourier y Método Whittaker: un toolbox escrito en pythonHumberto Cruz-Sanabria, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Santiago Belda, Juan Pablo Rivera-Caicedo, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoDifu100ci@, Revista de difusión científica, ingeniería y tecnologías, 2021El uso de series temporales utilizando datos ópticos ha sido de gran ayuda en el estudio de la variabilidad espacio-temporal de cultivos agrícolas a escala global. Un problema recurrente en el uso de datos ópticos es que son espacial y temporalmente discontinuos, con valores perdidos debido a multitud de factores como puede ser condiciones climáticas adversas, baja resolución temporal, fallos en el sensor, entre otras. Como consecuencia, se necesitan soluciones de relleno de huecos de datos para un monitoreo preciso de los cultivos. En el presente articulo se expone un toolbox de procesamiento de imágenes escrito en python. Éste permite realizar diferentes tareas en series temporales en productos Sentinel-2, las cuales incluyen: (1) generar series temporales con datos espacialmente continuos a partir de datos discontinuos utilizando dos métodos de interpolación: Series de Fourier y Whittaker, (2) detectar parámetros fenológicos (inicio de temporada, pico mas alto y fin de la temporada, es decir etapas clave de crecimiento del cultivo) y (3) Reconstruir mapas de algún índice espectral de un día del cual no se tengan datos. El toolbox ha sido probado en una zona cultivada con caña de azúcar, y los resultados muestran que el método Whittaker es que mejor interpola los datos. Este toolbox beneficiará a los agricultores para un mejor monitoreo del cultivo de la caña de azúcar, considerando todos los días del ciclo de desarrollo y expresado a través de un índice espectral.
@article{2021_difu100cia_2, author = {Cruz-Sanabria, Humberto and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Belda, Santiago and Rivera-Caicedo, Juan Pablo and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, title = {Interpolación de datos ópticos discontinuos mediante series de Fourier y Método Whittaker: un toolbox escrito en python}, journal = {Difu100ci@, Revista de difusi\'on cient\'ifica, ingenier\'ia y tecnolog\'ias}, year = {2021}, volume = {15}, number = {3}, pages = {140-146}, url = {http://difu100cia.uaz.edu.mx/index.php/difuciencia/article/view/213}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2020
- cica
 Traceability for the agricultural supply chain from a computer approachRaquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Francisco Cervantes-Zambrano, and René Gudiño VargasRevista de Tecnologías en Procesos Industriales, 2020
Traceability for the agricultural supply chain from a computer approachRaquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Francisco Cervantes-Zambrano, and René Gudiño VargasRevista de Tecnologías en Procesos Industriales, 2020Traceability is essential in the agricultural sector as a requirement in the supply chain, as it generates valuable information from cultivation to commercialization. In this paper we present a system that concentrates information on the different activities carried out in avocado orchards. The platform includes monitoring activities by connecting to a cloud database that allows access to the different processes that are recorded through a desktop application and a Web page. The system also controls the information that is generated in the maintenance log, as well as the supervision of the orchards through unmanned aerial vehicles that are currently essential to improve the conditions of the crops in the orchards. In this way, maintenance work is controlled efficiently, taking care of the environment through the proper use of fertilizers and other chemicals used in the agricultural field.
@article{2020_cica_rtpi, author = {Ochoa-Ornelas, Raquel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Cervantes-Zambrano, Francisco and Gudi\~no Vargas, Ren\'e}, journal = {Revista de Tecnolog\'ias en Procesos Industriales}, title = {Traceability for the agricultural supply chain from a computer approach}, year = {2020}, volume = {4}, number = {11}, pages = {1--7}, keywords = {Traceability, databases, orchards, maintenance, log}, doi = {10.35429/JTIP.2020.11.4.1.7}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - RevDesTec
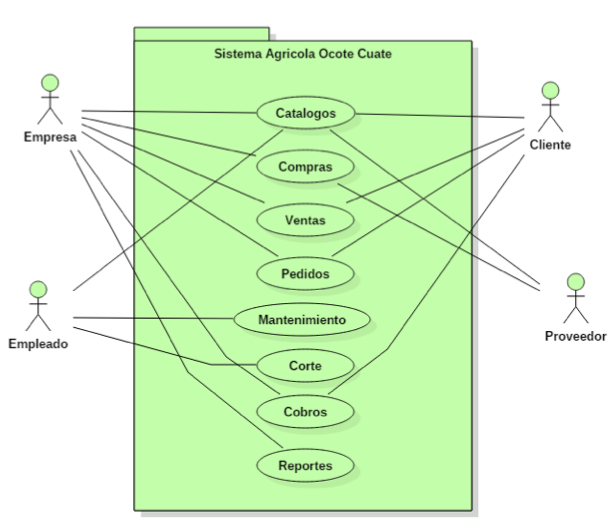 Implementation of Computer Applications in the Avocado Agriculture IndustryRaquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, and Jonathan Osornio-MendozaRevista del Desarrollo Tecnológico, 2020
Implementation of Computer Applications in the Avocado Agriculture IndustryRaquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, and Jonathan Osornio-MendozaRevista del Desarrollo Tecnológico, 2020Agriculture 4.0, conceived as a kind of industry, is built by integrating a set of digital technologies such as the Internet of things, Artificial Intelligence, and the management of large databases (or Big Data). This industry implies a transformation of the production infrastructure that allows increasing the agricultural productivity and the quality of the products efficiently and sustainably. These changes require the implementation of digital technologies for the collection, analysis and communication of information, allowing timely decision making. This article deals with the implementation of a platform that includes both desktop, Web and mobile applications and Internet of things tools for the control of production and marketing in avocado orchards. The development of a prototype of the platform is described under agile methodologies and following an iterative and incremental strategy. Finally, the tests that determine the integral functionality of the platform prototype and experimental results are presented.
@article{2020_rdt, author = {Ochoa-Ornelas, Raquel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and S\'anchez-Cervantes, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Osornio-Mendoza, Jonathan}, journal = {Revista del Desarrollo Tecnológico}, title = {Implementation of Computer Applications in the Avocado Agriculture Industry}, year = {2020}, volume = {3}, number = {9}, pages = {13--23}, keywords = {Agriculture 4.0, Connectivity, Database}, doi = {10.35429/JTD.2019.9.3.13.23}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - amcs
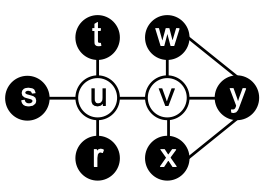 A Genetic Algorithm for the Maximum 2–Packing Set ProblemJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and J. Octavio Gutierrez-GarciaInternational Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2020
A Genetic Algorithm for the Maximum 2–Packing Set ProblemJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and J. Octavio Gutierrez-GarciaInternational Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2020Given an undirected connected graph G = (V,E), a subset of vertices S is a maximum 2-packing set if the number of edges in the shortest path between any pair of vertices in S is at least 3 and S has the maximum cardinality. In this paper, we present a genetic algorithm for the maximum 2-packing set problem on arbitrary graphs, which is an NP-hard problem. To the best of our knowledge, this work is a pioneering effort to tackle this problem for arbitrary graphs. For comparison, we extended and outperformed a well-known genetic algorithm originally designed for the maximum independent set problem. We also compared our genetic algorithm with a polynomial-time one for the maximum 2-packing set problem on cactus graphs. Empirical results show that our genetic algorithm is capable of finding 2-packing sets with a cardinality relatively close (or equal) to that of the maximum 2-packing sets. Moreover, the cardinality of the 2-packing sets found by our genetic algorithm increases linearly with the number of vertices and with a larger population and a larger number of generations. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical proof demonstrating that our genetic algorithm increases the fitness for each candidate solution when certain conditions are met.
@article{2020_amcs, author = {Trejo-S\'anchez, Joel Antonio and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Gutierrez-Garcia, J. Octavio}, title = {A Genetic Algorithm for the Maximum 2–Packing Set Problem}, journal = {International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Sciendo}, address = {Berlin}, volume = {30}, number = {1}, doi = {10.34768/amcs-2020-0014}, pages = {173--184}, keywords = {Maximum 2 packing set, Genetic algorithms, Graph algorithms}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - risti
 A systematic review of the literature focused on the use of unmanned aerial vehicles during the vegetation detection processEnrique Ponce-Corona, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Brenda Acevedo-Juárez, Miguel De-la-Torre, Himer Avila-George, and Wilson CastroRISTI - Revista Ibérica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informação, Mar 2020
A systematic review of the literature focused on the use of unmanned aerial vehicles during the vegetation detection processEnrique Ponce-Corona, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Brenda Acevedo-Juárez, Miguel De-la-Torre, Himer Avila-George, and Wilson CastroRISTI - Revista Ibérica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informação, Mar 2020In recent years, the use of unmanned aerial vehicles has become popular in the development of agricultural and forestry applications. Due to the importance of plants in both rural and urban environments, the extraction of information from remote sensing data is a relevant research area; such information is fundamental for urban and rural planning, establishing sustainable ecological niches, estimating crop yields, conducting forest inventories, monitoring agricultural management systems and some other agricultural applications. In this article, a systematic review of the literature concerning the use of unmanned aerial vehicles in applications related to vegetation detection and plant inventory is presented. Likewise, an analysis of the main computational and statistical techniques used for processing unmanned aerial vehicles images is also made.
@article{2020_risti, title = {A systematic review of the literature focused on the use of unmanned aerial vehicles during the vegetation detection process}, journal = {RISTI - Revista Ib\'erica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informa\c{c}\~ao}, author = {Ponce-Corona, Enrique and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Acevedo-Ju\'arez, Brenda and De-la-Torre, Miguel and Avila-George, Himer and Castro, Wilson}, issn = {1646-9895}, language = {es}, year = {2020}, month = mar, pages = {82--101}, publisher = {scielopt}, keywords = {Unmanned aerial vehicles, vegetation, counting, inventory, image processing, algorithms}, doi = {10.17013/risti.36.82-101}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ceur
 TecNM at MEX-A3T 2020: Fake News and Aggressiveness Analysis in Mexican SpanishSamuel Arce-Cardenas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Miguel Ángel Álvarez CarmonaIn Proceedings of the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF 2020) co-located with 36th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing (SEPLN 2020), Málaga, Spain, September 23th, 2020 , Mar 2020
TecNM at MEX-A3T 2020: Fake News and Aggressiveness Analysis in Mexican SpanishSamuel Arce-Cardenas, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Miguel Ángel Álvarez CarmonaIn Proceedings of the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF 2020) co-located with 36th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing (SEPLN 2020), Málaga, Spain, September 23th, 2020 , Mar 2020This paper explains our approach to Aggressiveness Identification and Fake News Classification in the 2020 MEX-A3T shared task. The tasks propose a binary classification for both tasks (aggressive and non-aggressive or fake news and non-fake news). We approached the problem using simple basic methods of features selection and terms weighing. We trained with a set of machine learning algorithms. Our best run for aggressiveness identification achieved an accuracy of 0.81, where the best result obtained 0.88. On the other hand, for the aggressiveness identification, our accuracy result was 0.78, where the best result was 0.85.
@inproceedings{2020_ceur2, author = {Arce{-}Cardenas, Samuel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and \'Alvarez Carmona, Miguel \'Angel}, editor = {{\'{A}}ngel Garc{\'{\i}}a Cumbreras, Miguel and Gonzalo, Julio and C{\'{a}}mara, Eugenio Mart{\'{\i}}nez and Mart{\'{\i}}nez{-}Unanue, Raquel and Rosso, Paolo and Zafra, Salud M. Jim{\'{e}}nez and Zambrano, Jenny Alexandra Ortiz and Miranda, Antonio and Zamorano, Jordi Porta and Guti{\'{e}}rrez, Yoan and Ros{\'{a}}, Aiala and Montes{-}y{-}G{\'{o}}mez, Manuel and Vega, Manuel Garc{\'{\i}}a}, title = {TecNM at {MEX-A3T} 2020: Fake News and Aggressiveness Analysis in Mexican Spanish}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF 2020) co-located with 36th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing {(SEPLN} 2020), M{\'{a}}laga, Spain, September 23th, 2020}, series = {CEUR Workshop Proceedings}, volume = {2664}, pages = {265--272}, publisher = {CEUR-WS.org}, year = {2020}, keywords = {Aggressiveness Identification, Fake News Classification, Natural Language Processing}, url = {http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2664/mexa3t\_paper5.pdf}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ceur
 ITCG’s Participation at MEX-A3T 2020: Aggressive Identification and Fake News Detection Based on Textual Features for Mexican SpanishDiego Zaizar-Gutiérrez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Miguel Ángel Álvarez CarmonaIn Proceedings of the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF 2020) co-located with 36th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing (SEPLN 2020), Málaga, Spain, September 23th, 2020 , Mar 2020
ITCG’s Participation at MEX-A3T 2020: Aggressive Identification and Fake News Detection Based on Textual Features for Mexican SpanishDiego Zaizar-Gutiérrez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Miguel Ángel Álvarez CarmonaIn Proceedings of the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF 2020) co-located with 36th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing (SEPLN 2020), Málaga, Spain, September 23th, 2020 , Mar 2020This paper describes our participation in the MEX-A3T 2020 for the tasks of identification of aggressive-ness and fake news in Mexican Spanish tweets. We evaluate the combination of basic text classification techniques, including six machine learning algorithms, two methods for keyword extractions, and two preprocessing techniques. Our best run showed an F1-macro score of 0.754 for aggressiveness and 0.815 for fake news. Our preliminary results are satisfactory and competitive with other participating teams.
@inproceedings{2020_ceur1, author = {Zaizar-Guti\'errez, Diego and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and \'Alvarez Carmona, Miguel \'Angel}, editor = {{\'{A}}ngel Garc{\'{\i}}a Cumbreras, Miguel and Gonzalo, Julio and C{\'{a}}mara, Eugenio Mart{\'{\i}}nez and Mart{\'{\i}}nez{-}Unanue, Raquel and Rosso, Paolo and Zafra, Salud M. Jim{\'{e}}nez and Zambrano, Jenny Alexandra Ortiz and Miranda, Antonio and Zamorano, Jordi Porta and Guti{\'{e}}rrez, Yoan and Ros{\'{a}}, Aiala and Montes{-}y{-}G{\'{o}}mez, Manuel and Vega, Manuel Garc{\'{\i}}a}, title = {ITCG's Participation at {MEX-A3T} 2020: Aggressive Identification and Fake News Detection Based on Textual Features for Mexican Spanish}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF 2020) co-located with 36th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing {(SEPLN} 2020), M{\'{a}}laga, Spain, September 23th, 2020}, series = {CEUR Workshop Proceedings}, volume = {2664}, pages = {258--264}, publisher = {CEUR-WS.org}, year = {2020}, keywords = {Aggressiveness Identification, Fake News Classification, Natural Language Processing}, url = {http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2664/mexa3t\_paper4.pdf}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - rpc
 A hybrid genetic algorithm to reduce the radiation dose in CR imagesMaría Guadalupe Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Vicente Vidal, and Gumersindo VerdúRadiation Physics and Chemistry, Mar 2020Special issue dedicated to the 14th International Symposium on Radiation Physics
A hybrid genetic algorithm to reduce the radiation dose in CR imagesMaría Guadalupe Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, Vicente Vidal, and Gumersindo VerdúRadiation Physics and Chemistry, Mar 2020Special issue dedicated to the 14th International Symposium on Radiation PhysicsThe quality of computed radiography (CR) images typically relate to patient radiation exposure. The lower the X-ray dose exposure, the higher the level of inherent noise in the CR images. In this work, we address the noise reduction problem by using an estimation of the standard deviation in CR images as an objective function to minimize. We propose a hybrid genetic algorithm for this aim, which produces improved versions of CR images. We also applied an edge-detection method based on the Canny algorithm to preserve the edges of the original CR images. We executed our proposed algorithm for CR images obtained under different radiation exposures. Experimental results show that our solution improves lower radiation CR images reaching a quality as similar to those with higher radiation doses.
@article{2019_rpc, title = {A hybrid genetic algorithm to reduce the radiation dose in CR images}, journal = {Radiation Physics and Chemistry}, volume = {167}, pages = {108275}, year = {2020}, note = {Special issue dedicated to the 14th International Symposium on Radiation Physics}, issn = {0969-806X}, doi = {10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.04.025}, author = {S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Vidal, Vicente and Verd\'u, Gumersindo}, keywords = {Computed radiography, Radiation dose, Evolutionary algorithms}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2019
- ijstre
 Multiclassification of mammographic density levels with genetic programmingNinderlisbeth Vargas Cardenas, María Guadalupe Sánchez, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoInternational Journal of Scientific and Technical Research in Engineering, Mar 2019
Multiclassification of mammographic density levels with genetic programmingNinderlisbeth Vargas Cardenas, María Guadalupe Sánchez, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoInternational Journal of Scientific and Technical Research in Engineering, Mar 2019Breast cancer is the most frequent in women, as well as cervical and skin cancer. Medical research for the prevention of breast cancer has shown that breast density is a strong indicator of cancer risk. The density can be evaluated through the classification proposed by the American College of Radiology (ACR). The objective of this article is to show the results obtained from the multiclassification of mammographic density levels using genetic programming. The multiclass classification starts from a set of texture characteristics of the mammographic images. Various methods of feature extraction and classification have been implemented. The features of the images are the input for the classifiers. For the experiments, the INbreast mammography database was used. The results show good classification and will help doctors to make a reliable diagnosis of cancer risk.
@article{2019_ijstre, title = {Multiclassification of mammographic density levels with genetic programming}, author = {Vargas Cardenas, Ninderlisbeth and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, journal = {International Journal of Scientific and Technical Research in Engineering}, volume = {4}, number = {3}, pages = {31--37}, year = {2019}, keywords = {Breast Density, Genetic Programming, Multiclassification}, url = {http://www.ijstre.com/Publish/4302019/246886609.pdf}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - ingeniantes
 Metodología para obtener mapas del índice de área foliar en cultivos de caña de azúcarRodrigo Rodriguez-Ramirez, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Himer Avila-George, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Rubén Zepeda-GarcíaIngeniantes, Mar 2019
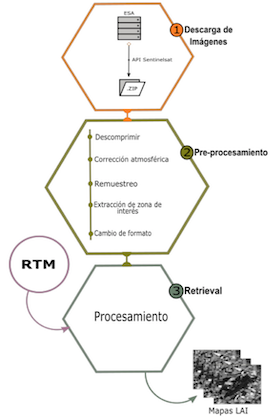
Metodología para obtener mapas del índice de área foliar en cultivos de caña de azúcarRodrigo Rodriguez-Ramirez, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Himer Avila-George, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Rubén Zepeda-GarcíaIngeniantes, Mar 2019In recent years, remote sensing has become a fundamental tool for the development of precision agriculture. Through crop information, crop prediction models can be developed, plant photosynthetic capacity can be estimated, and the relationship between biomass accumulation and yield under certain environmental conditions can be understood. It can be achieved through the estimation of a vegetation index called the leaf area index (LAI) using remote sensing techniques and from the map of the region of interest. However, remote sensing has some limitations in terms of spatial, spectral, and temporal resolution of the available images. Earth observation satellites offer multitemporal images that are used to assess and monitor the state of vegetation. Sentinel-2 satellites of the European Space Agency are part of these technologies. This article proposes a methodology with free software libraries for the processing of images obtained from Sentinel-2 to get the LAI map of the sugarcane crop. The methodology consists of three phases, (1) download, (2) preprocessing, and (3) retrieval model. The results show that through the methodology implemented, the LAI map of the area of interest planted with sugar cane can be obtained.
@article{2019_ingeniantes, title = {Metodolog\'ia para obtener mapas del \'indice de \'area foliar en cultivos de ca\~na de az\'ucar}, author = {Rodriguez-Ramirez, Rodrigo and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Avila-George, Himer and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Zepeda-Garc\'ia, Rub\'en}, journal = {Ingeniantes}, volume = {2}, number = {2}, pages = {144--149}, year = {2019}, keywords = {Sugarcane, satellite images, LAI maps, image processing, Sentinel-2, remote sensing}, url = {http://citt.itsm.edu.mx/ingeniantes/pdfversion/ingeniantes6no2vol2-esp.pdf}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - cimps
 Detection of Vegetation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Images: A Systematic ReviewEnrique Ponce-Corona, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, W Castro, Miguel De-la-Torre, and Himer Avila-GeorgeIn 2019 8th International Conference On Software Process Improvement (CIMPS) , Mar 2019
Detection of Vegetation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Images: A Systematic ReviewEnrique Ponce-Corona, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, W Castro, Miguel De-la-Torre, and Himer Avila-GeorgeIn 2019 8th International Conference On Software Process Improvement (CIMPS) , Mar 2019In recent years, the use of unmanned aerial vehicles for the development of agricultural and forestry applications has become popular. Given the importance of plants in both rural and urban environments, the extraction of information from data obtained by remote sensing is a highly relevant area of research. Such information is vital in urban and rural planning activities, the establishment of sustainable ecological niches, estimation of crop yields, the realization of forest inventories, the supervision of agricultural management systems, and some other agricultural applications. In this paper, we present a systematic review of the literature regarding the use of unmanned aerial vehicles in applications related to the detection of vegetation and plants inventory. Likewise, an analysis of the software used and the main computational and statistical techniques for the processing of images taken from unmanned aerial vehicles is made.
@inproceedings{2019_cimps2, author = {Ponce-Corona, Enrique and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Castro, W and De-la-Torre, Miguel and Avila-George, Himer}, booktitle = {2019 8th International Conference On Software Process Improvement (CIMPS)}, title = {Detection of Vegetation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Images: A Systematic Review}, year = {2019}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1--7}, publisher = {IEEE}, isbn = {978-1-7281-5555-5}, doi = {10.1109/CIMPS49236.2019.9082434}, keywords = {Vegetation, counting, inventory, image processing}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - cimps
 Automating an Image Processing Chain of the Sentinel-2 SatelliteRodrigo Rodriguez-Ramirez, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Juan Pablo Rivera-Caicedo, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Himer Avila-GeorgeIn Trends and Applications in Software Engineering , Mar 2019
Automating an Image Processing Chain of the Sentinel-2 SatelliteRodrigo Rodriguez-Ramirez, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Juan Pablo Rivera-Caicedo, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Himer Avila-GeorgeIn Trends and Applications in Software Engineering , Mar 2019In this paper, a chain of satellite image processing using free software libraries is proposed, to estimate biophysical parameters using data from the Sentinel-2 satellite. In particular, the processing chain proposed allows atmospheric correction, resampling and spatial cropping of satellite images. To evaluate the functionality of the developed processing chain, the sugarcane cultivation of the Mexican region of Jalisco is introduced as a case study; from the selected scene, the leaf area index (LAI) is estimated using a model based on the Gaussian Process Regression technique, which is trained employing synthetic reflectance data created utilizing the PROSAIL radiative transfer model.
@inproceedings{2019_cimps, author = {Rodriguez-Ramirez, Rodrigo and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Rivera-Caicedo, Juan Pablo and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Avila-George, Himer}, editor = {Mejia, Jezreel and Mu{\~{n}}oz, Mirna and Rocha, \'Alvaro and Pe{\~{n}}a, Adriana and P\'erez-Cisneros, Marco}, title = {Automating an Image Processing Chain of the Sentinel-2 Satellite}, booktitle = {Trends and Applications in Software Engineering}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {216--224}, keywords = {Sentinel-2, LAI, PROSAIL, Image processing, chain Gaussian process}, isbn = {978-3-030-01171-0}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-01171-0_20}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2018
- ijcopi
 A multi-agent architecture for scheduling of high performance services in a GPU clusterJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, José Luis López-Martínez, José Octavio Gutiérrez-García, Julio César Ramírez-Pacheco, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoInternational Journal of Combinatorial Optimization Problems and Informatics, Jan 2018
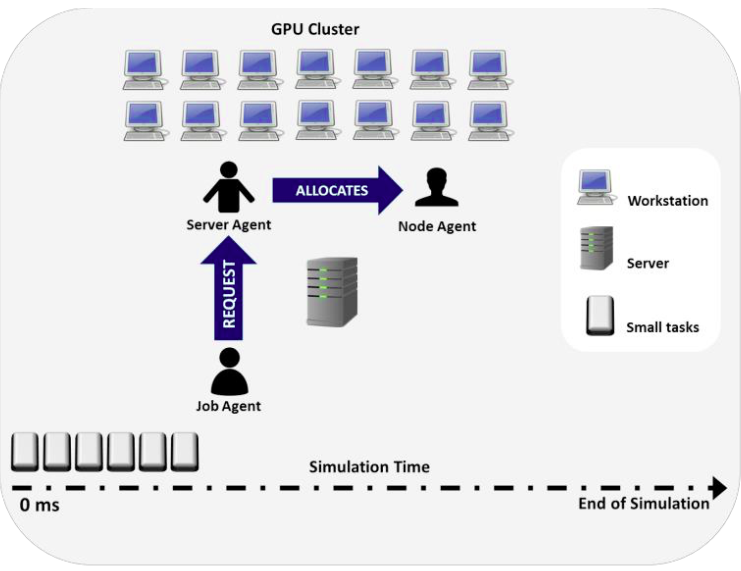
A multi-agent architecture for scheduling of high performance services in a GPU clusterJoel Antonio Trejo-Sánchez, José Luis López-Martínez, José Octavio Gutiérrez-García, Julio César Ramírez-Pacheco, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoInternational Journal of Combinatorial Optimization Problems and Informatics, Jan 2018Nowadays, clusters containing multiple GPU nodes are widely used to execute high-performance computing applications. Diverse disciplines use these clusters to improve the performance of several services that consume high computational resources. The challenge of executing high-performance computing applications becomes harder when the applications are executed concurrently and each one of them may demand multiple GPU nodes for different periods of time. To tackle this challenge, we propose a multi-agent architecture for scheduling multiple services in a heterogeneous GPU cluster. We provide simulation results of our agent-based system utilizing three commonly used scheduling heuristics for several configuration settings.
@article{2018_ijcopi, author = {Trejo-S\'anchez, Joel Antonio and L\'opez-Mart\'inez, Jos\'e Luis and Guti\'errez-García, Jos\'e Octavio and Ram\'irez-Pacheco, Julio C\'esar and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, title = {A multi-agent architecture for scheduling of high performance services in a GPU cluster}, volume = {9}, url = {https://ijcopi.org/index.php/ojs/article/view/75}, number = {1}, journal = {International Journal of Combinatorial Optimization Problems and Informatics}, year = {2018}, month = jan, pages = {12--22}, keywords = {High performance computing, scheduling}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - jcst
 A Two-Player Coalition Cooperative Scheme for the Bodyguard Allocation ProblemJosé Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Daniel Brubeck-Salcedo, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Héctor Zatarain-AcevesJournal of Computer Science and Technology, Jul 2018
A Two-Player Coalition Cooperative Scheme for the Bodyguard Allocation ProblemJosé Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Daniel Brubeck-Salcedo, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Héctor Zatarain-AcevesJournal of Computer Science and Technology, Jul 2018We address the bodyguard allocation problem (BAP), an optimization problem that illustrates the conflict of interest between two classes of processes with contradictory preferences within a distributed system. While a class of processes prefers to minimize its distance to a particular process called the root, the other class prefers to maximize it; at the same time, all the processes seek to build a communication spanning tree with the maximum social welfare. The two state-of-the-art algorithms for this problem always guarantee the generation of a spanning tree that satisfies a condition of Nash equilibrium in the system; however, such a tree does not necessarily produce the maximum social welfare. In this paper, we propose a two-player coalition cooperative scheme for BAP, which allows some processes to perturb or break a Nash equilibrium to find another one with a better social welfare. By using this cooperative scheme, we propose a new algorithm called FFC-BAPS for BAP. We present both theoretical and empirical analyses which show that this algorithm produces better quality approximate solutions than former algorithms for BAP.
@article{2018_jcst, author = {Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Brubeck-Salcedo, Daniel and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Zatarain-Aceves, H\'ector}, title = {A Two-Player Coalition Cooperative Scheme for the Bodyguard Allocation Problem}, journal = {Journal of Computer Science and Technology}, year = {2018}, month = jul, day = {01}, volume = {33}, number = {4}, pages = {823--837}, issn = {1860-4749}, doi = {10.1007/s11390-018-1858-8}, keywords = {bodyguard allocation problem, coalitional game, graph algorithm, Nash equilibrium}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - jsep
 Analysis of the changes in communication and social interactions during the transformation of a traditional team into an agile teamIsmael Edrein Espinosa-Curiel, Josefina Rodríguez-Jacobo, Erika Vázquez-Alfaro, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoJournal of Software: Evolution and Process, Jul 2018e1946 smr.1946
Analysis of the changes in communication and social interactions during the transformation of a traditional team into an agile teamIsmael Edrein Espinosa-Curiel, Josefina Rodríguez-Jacobo, Erika Vázquez-Alfaro, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoJournal of Software: Evolution and Process, Jul 2018e1946 smr.1946Traditional software teams that implement agile methodologies frequently experience difficulty working efficiently as agile teams. While agile methodologies support and promote social activities and behaviors, the understanding of the social phenomena and challenges that arise during the transformation of traditional teams into agile teams is limited. We conducted an extensive 10-month case study in a software enterprise to analyze the changes in the communication and social interactions of employees during the transformation process, and to delineate the social challenges that arise during this process. Using social interaction registers, we collected data on the communication and social interactions of employees, first when they worked as a traditional team and then as an agile team. Then, we processed the data using social network analysis methods to identify the differences between these 2 types of teams and to create graphs of communication and social interaction networks. We identified that the transformation process influences formal, informal, oral, and written communication and increases conjunctive and disjunctive social interactions. Further, from the results of interviews conducted with all the enterprise members, we identified 5 social challenges to transforming a traditional team into an agile one. The results of this research suggest that the transformation process requires broad changes in the relationships and interactions among employees.
@article{2018_jsep, author = {Espinosa-Curiel, Ismael Edrein and Rodr\'iguez-Jacobo, Josefina and V\'azquez-Alfaro, Erika and Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, title = {Analysis of the changes in communication and social interactions during the transformation of a traditional team into an agile team}, journal = {Journal of Software: Evolution and Process}, year = {2018}, volume = {30}, number = {9}, pages = {e1946}, keywords = {agile software development, communication, social interactions, social network analysis, team transformation}, doi = {10.1002/smr.1946}, eprint = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/smr.1946}, note = {e1946 smr.1946}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - icaisc
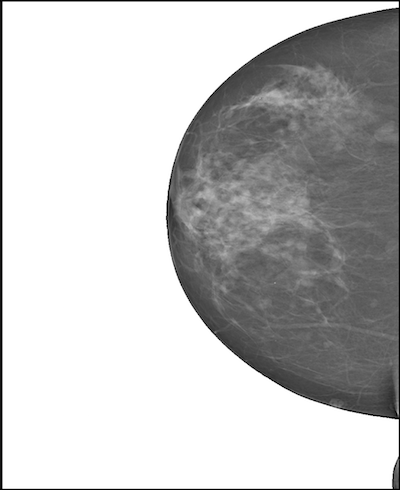 Genetic Programming for the Classification of Levels of Mammographic DensityDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Raquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Ismael Edrein Espinosa-Curiel, and Vicente VidalIn Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing , Jul 2018
Genetic Programming for the Classification of Levels of Mammographic DensityDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez, Raquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Ismael Edrein Espinosa-Curiel, and Vicente VidalIn Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing , Jul 2018Breast cancer is the second cause of death of adult women in Mexico. Some of the risk factors for breast cancer that are visible in a mammography are the masses, calcifications, and the levels of mammographic density. While the first two have been studied extensively through the use of digital mammographies, this is not the case for the last one. In this paper, we address the automatic classification problem for the levels of mammographic density based on an evolutionary approach. Our solution comprises the following stages: thresholding, feature extractions, and the implementation of a genetic program. We performed experiments to compare the accuracy of our solution with other conventional classifiers. Experimental results show that our solution is very competitive and even outperforms the other classifiers in some cases.
@inproceedings{2018_icaisc, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Ochoa-Ornelas, Raquel and Espinosa-Curiel, Ismael Edrein and Vidal, Vicente}, editor = {Rutkowski, Leszek and Scherer, Rafa{\l} and Korytkowski, Marcin and Pedrycz, Witold and Tadeusiewicz, Ryszard and Zurada, Jacek M.}, title = {Genetic Programming for the Classification of Levels of Mammographic Density}, booktitle = {Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing}, year = {2018}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {363--375}, isbn = {978-3-319-91253-0}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-91253-0_34}, keywords = {Breast cancer, Levels of mammographic density, Genetic programming}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - cica
 Plataforma estratégica para optimizar la contratación de serviciosRaquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Luis Azael Jiménez-Fajardo, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoRevista de Simulación Computacional, Jul 2018
Plataforma estratégica para optimizar la contratación de serviciosRaquel Ochoa-Ornelas, Luis Azael Jiménez-Fajardo, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoRevista de Simulación Computacional, Jul 2018Smart Cities have been developed through the accelerated use of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), providing high efficiency public services, which also include security, productivity, and co mpetiti veness. A S mart City is formed with the increase of investments in education, infrastructure, energy control, technologies and transportation, promoting a better quality of life. In the same way, sustainable economic development, which promotes a prudent and reflective social participation of the environment, together with a tenacious and committed government that offers safe and quality services, optimizing times and resources, results in a Smart City. In this article, the Toc-Toc platform is presented to provide services through mobile, Web and desk applications. The platform helps the continuous improvement in the quality of the services offering seriousness and security for the users who request it, encouraging the local companies to be more competitive, generating jobs and improving the economic and social level of the region.
@article{2018_cica, author = {Ochoa-Ornelas, Raquel and Jim\'enez-Fajardo, Luis Azael and S\'anchez-Cervantes, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, journal = {Revista de Simulaci\'on Computacional}, title = {Plataforma estrat\'egica para optimizar la contrataci\'on de servicios}, year = {2018}, volume = {2}, number = {3}, pages = {1--10}, url = {https://www.ecorfan.org/taiwan/research_journals/Simulacion_Computacional/vol2num3/Revista_de_Simulaci\%C3\%B3n_Computacional_V2_N3.pdf}, keywords = {Smart City, Web, Mobile, Services}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2017
- cica
 Estudio comparativo de árboles de decisión para la clasificación de densidad mamográficaMaría Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Raquel Ochoa-OrnelasRevista de Tecnologías de la Información, Jul 2017
Estudio comparativo de árboles de decisión para la clasificación de densidad mamográficaMaría Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, and Raquel Ochoa-OrnelasRevista de Tecnologías de la Información, Jul 2017Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in women after cervical cancer, and its trend in Mexico is increasing. There are several risk factors that allow the detection of early stages of breast cancer; among the main ones are the masses, calcifications and mammographic densities visible from an image. Currently, the computer-aided diagnosis has proved to be a useful tool in support of an experienced physician for the early detection of breast cancer. Several classification algorithms are used for the detection of early stages of breast cancer. However, the classification of mammary densities has been the least studied. Recent studies of classification methods for mammographic density levels consist of a stage of pre-processing of the image, extraction of characteristics, and choice of an efficient algorithm for classification. In the present paper, we perform a comparative study of some decision trees considering the statistical features of the image for the classification of mammographic density levels.
@article{2017_cica, author = {S\'anchez-Cervantes, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Ochoa-Ornelas, Raquel}, journal = {Revista de Tecnolog\'ias de la Informaci\'on}, title = {Estudio comparativo de \'arboles de decisi\'on para la clasificaci\'on de densidad mamogr\'afica}, year = {2017}, volume = {4}, number = {10}, pages = {45--53}, keywords = {Breast cancer, decision trees, mammographic densities}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - riit
 Modelo para la ejecución de pruebas de softwareOscar Paul Jiménez-Bibián, Noé García-Díaz, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, and José de Jesús García-VirgenRevista Internacional de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica, Jul 2017
Modelo para la ejecución de pruebas de softwareOscar Paul Jiménez-Bibián, Noé García-Díaz, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, and José de Jesús García-VirgenRevista Internacional de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica, Jul 2017Software testing is a critical element to guarantee the quality of software. The need of companies to develop software with quality has motivated the study of several methods for the development and execution of software testing. Implementing these methods requires defining the process to improve and control the phases of the software testing and their execution order, which is a hard task. In this paper, we propose a new method for the development and implementation of software testing. This method consists of the combination of the models TMMi (testing maturity model integrated), MoProSoft (software process model) and the software testing process for the university environment. In comparison with these models, our proposed method is adaptable for software developments for small to medium scale projects. It also adapts to the software development for different platforms, such as Web, mobile, and desktop. We show the effectivity of our proposed method through a study case for the website Allison. This website is a software developed by the mexican company Maldonado Sofware. As an additional contribution, we proposed a new classification of software testing according to its type of black box or white box testing. We performed 51 software testing from which, we identified 28 different types of failures. The results of the study case show the effectivity of our proposed method.
@article{2017_riiit, author = {Jim\'enez-Bibi\'an, Oscar Paul and Garc\'ia-D\'iaz, No\'e and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and S\'anchez-Cervantes, Mar\'ia Guadalupe and Garc\'ia-Virgen, Jos\'e de Jes\'us}, title = {Modelo para la ejecuci\'on de pruebas de software}, journal = {Revista Internacional de Investigaci\'on e Innovaci\'on Tecnol\'ogica}, year = {2017}, volume = {5}, number = {28}, pages = {1--12}, keywords = {Modelos de pruebas de software, calidad de software, herramientas de prueba}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2016
- wcci
 A hybrid genetic algorithm for color image denoisingDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, María G. Sánchez, Jesus Ezequiel Molinar-Solis, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Vicente Vidal, and Gumersindo VerdúIn 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC) , Jul 2016
A hybrid genetic algorithm for color image denoisingDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, María G. Sánchez, Jesus Ezequiel Molinar-Solis, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Vicente Vidal, and Gumersindo VerdúIn 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC) , Jul 2016In this paper, we address the problem of impulsive noise reduction in color images through an evolutionary approach. We designed a new hybrid genetic algorithm, called GARIN, which takes as input a noisy image and generates as output a reduced noise version of the same image. As part of its evolutionary process, GARIN integrates the execution of robust and adaptive filters from literature with the aim to combine and improve their results. Unlike most genetic algorithms designed for color image denoising, our algorithm evolves a set of images instead of the set of parameters of the filters. Experimental results show that, compared with other filters of literature, the algorithm GARIN efficiently removes impulsive noise in color images while, at the same time, it preserves their main features.
@inproceedings{2016_wcci, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and S\'anchez, Mar\'ia G. and Molinar-Solis, Jesus Ezequiel and Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Vidal, Vicente and Verdú, Gumersindo}, booktitle = {2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC)}, title = {A hybrid genetic algorithm for color image denoising}, year = {2016}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {3879--3886}, keywords = {Hybrid genetic algorithm, image denoising, impulsive noise}, doi = {10.1109/CEC.2016.7744281}, issn = {}, month = jul, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2015
- asoc
 A cascade evolutionary algorithm for the bodyguard allocation problemHéctor Zatarain-Aceves, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Carlos A. Brizuela, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoApplied Soft Computing, Jul 2015
A cascade evolutionary algorithm for the bodyguard allocation problemHéctor Zatarain-Aceves, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Carlos A. Brizuela, and Daniel Fajardo-DelgadoApplied Soft Computing, Jul 2015The bodyguard allocation problem (BAP) is an optimization problem that illustrates the behavior of processes with contradictory individual goals in some distributed systems. The objective function of this problem is the maximization of a parameter called the social welfare. Although the main method proposed to solve this problem, known as CBAP, is simple and time efficient, it lacks the ability to generate a diverse set of solutions, which is one of the most important feature to improve the chances to reach the global optimum. To overcome this drawback, we address the BAP with an evolutionary algorithm, the EBAP. Later, we take advantage of the best properties of both algorithms, EBAP and CBAP, to generate a two-stage cascade evolutionary algorithm called FFC-BAP. Extensive experimental results show that the algorithm FFC-BAP outperforms both the EBAP and the CBAP, in terms of quality of solutions.
@article{2016_asoc, author = {Zatarain-Aceves, H\'ector and Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Brizuela, Carlos A. and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel}, title = {A cascade evolutionary algorithm for the bodyguard allocation problem}, journal = {Applied Soft Computing}, volume = {37}, pages = {643--651}, year = {2015}, issn = {1568-4946}, doi = {10.1016/j.asoc.2015.08.056}, keywords = {Bodyguard allocation problem, Evolutionary algorithm, Cascade evolutionary algorithm}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2013
- nousitz
 Diseño de una interfaz para el control de mensajes de texto a través de la API WMAL. Gama-Moreno, D. Fajardo-Delgado, C. Noguerón González, F.J. Cartujano Escobar, and M. Ménez EsquivelNousitz, Jul 2013
Diseño de una interfaz para el control de mensajes de texto a través de la API WMAL. Gama-Moreno, D. Fajardo-Delgado, C. Noguerón González, F.J. Cartujano Escobar, and M. Ménez EsquivelNousitz, Jul 2013El servicio de mensajes de texto (SMS) es hoy en día uno de los medios de comunicación más utilizados en el mundo, esto por la comodidad, economía y estabilidad del servicio, todo ello a pesar de que no ha sido posible explotar en su totalidad las ventajas que este servicio proporciona. Desafortunadamente, hay veces que la urgencia del usuario por enviar un mensaje de texto, es intervenida por la aplicación que controla los SMS en su dispositivo móvil. En este trabajo se propone implementar un API denominada Wireless Messaging API, la cual permite establecer comunicación vía sms entre dispositivos móviles, además de permitir al usuario programar una aplicación personalizada para controlar sus mensajes de texto. Así mismo se presenta el aprovechamiento del servicio de mensajes de texto combinado con la implementación de la API WMA para controlar dispositivos electrónicos a través SMS.
@article{2013_nousitz, author = {Gama-Moreno, L. and Fajardo-Delgado, D. and Noguerón González, C. and Cartujano Escobar, F.J. and Ménez Esquivel, M.}, journal = {Nousitz}, title = {Diseño de una interfaz para el control de mensajes de texto a través de la API WMA}, year = {2013}, volume = {1}, number = {54}, pages = {250--257}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, } - tpds
 The Bodyguard Allocation ProblemDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Anu G. BourgeoisIEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Jul 2013
The Bodyguard Allocation ProblemDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Anu G. BourgeoisIEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Jul 2013In this paper, we introduce the Bodyguard Allocation Problem (BAP) game, that illustrates the behavior of processes with contradictory individual goals in distributed systems. In particular, the game deals with the conflict of interest between two classes of processes that maximize/minimize their distance to a special process called the root. A solution of the BAP game represents a rooted spanning tree in which there exists a condition of equilibrium with maximum social welfare. We analyze the inefficiency of equilibria of the game based on both a completely cooperative and noncooperative approach. Additionally, we design two algorithms, CBAP and DBAP, that provide approximated solutions for the BAP game. We prove that both algorithms always terminate in a configuration with equilibrium and we analyze their running time based on the approach of cooperation used. We perform experimental simulations to compare the overall quality of equilibria obtained by the proposed algorithms.
@article{2013_tpds, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Bourgeois, Anu G.}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems}, title = {The Bodyguard Allocation Problem}, year = {2013}, volume = {24}, number = {7}, pages = {1465--1478}, keywords = {Distributed applications, game theory, distributed algorithms, bodyguard allocation problem}, doi = {10.1109/TPDS.2012.165}, issn = {1045-9219}, month = jul, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2012
- ijfcs
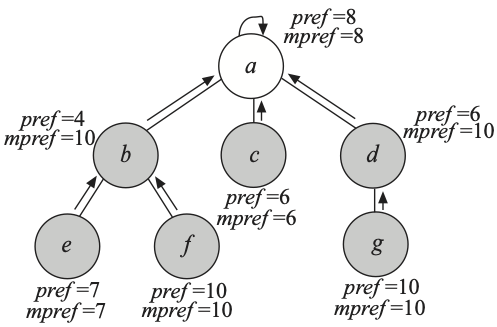 Randomized self-stabilizing leader election in preference-based anonymous treesDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Anu G. BourgeoisInternational Journal of Foundations of Computer Science, Jul 2012
Randomized self-stabilizing leader election in preference-based anonymous treesDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Anu G. BourgeoisInternational Journal of Foundations of Computer Science, Jul 2012The performance of processors in a distributed system can be measured by parameters such as bandwidth, storage capacity, work capability, reliability, power limitations, years of usage, among others. Each processor defines its preference based on these parameters. The preference represents an indicator of the quality of service that a processor can provide. An algorithm that follows a preference-based approach uses the preference of the processors to make decisions. In this paper we introduce a randomized self-stabilizing leader election algorithm for preference-based anonymous trees. Our algorithm assures that the processor with the highest preference in the system is always selected as the leader; moreover, it is able to solve symmetric configurations where each preference is the same. We prove that our algorithm has an optimal average time complexity and we also performed simulations to illustrate the average performance of the algorithm.
@article{2012_ijfcs, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Bourgeois, Anu G.}, title = {Randomized self-stabilizing leader election in preference-based anonymous trees}, journal = {International Journal of Foundations of Computer Science}, volume = {23}, number = {04}, pages = {853--875}, year = {2012}, doi = {10.1142/S0129054112400394}, keywords = {Leader election, self-stabilization, preference-based systems}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2010
- ipdps
 Randomized self-stabilizing leader election in preference-based anonymous treesDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Anu G. BourgeoisIn 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel Distributed Processing, Workshops and Phd Forum (IPDPSW) , Apr 2010
Randomized self-stabilizing leader election in preference-based anonymous treesDaniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, and Anu G. BourgeoisIn 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel Distributed Processing, Workshops and Phd Forum (IPDPSW) , Apr 2010The performance of processors in a distributed system can be measured by parameters such as bandwidth, storage capacity, work capability, reliability, manufacture technology, years of usage, among others. An algorithm using a preference-based approach uses these parameters to make decisions. In this paper we introduce a randomized self-stabilizing leader election algorithm for preference-based anonymous trees. Our algorithm uses the preference of the processors as criteria to select a leader under symmetric or non-symmetric configurations. It is partially inspired on Xu and Srimani’s algorithm, but we use a distributed daemon and randomization to break symmetry. We prove that our algorithm has an optimal average complexity time and performed simulations to verify our results.
@inproceedings{2010_ipdps, author = {Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Bourgeois, Anu G.}, booktitle = {2010 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel Distributed Processing, Workshops and Phd Forum (IPDPSW)}, title = {Randomized self-stabilizing leader election in preference-based anonymous trees}, year = {2010}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1--8}, keywords = {Leader Election, Self-Stabilization, Preference-Based Systems}, doi = {10.1109/IPDPSW.2010.5470838}, issn = {}, month = apr, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2005
- ijfcs
 Efficient simulation of an acyclic directed reconfigurable model on an undirected reconfigurable modelJosé Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Antonio Cárdenas-Haro, and Anu G. BourgeoisInternational Journal of Foundations of Computer Science, Apr 2005
Efficient simulation of an acyclic directed reconfigurable model on an undirected reconfigurable modelJosé Alberto Fernández-Zepeda, Daniel Fajardo-Delgado, José Antonio Cárdenas-Haro, and Anu G. BourgeoisInternational Journal of Foundations of Computer Science, Apr 2005In this paper we present a simulation of an acyclic n×n DR-Mesh on an n×n LR-Mesh. The simulation is efficient in regards to size since both models use the same number of processors. The worst execution time for this simulation is O(n2) time, but we demonstrate that its average execution time is O(logn). The fastest existing simulation takes O(logn) time, but it uses an extremely large number of processors. On the other hand, the most efficient simulation in terms of size takes O(log2n) time with O(n4/log2n) processors. Both of the existing simulations are for the unrestricted DR-Mesh. This paper provides an important step towards efficiently simulating the unrestricted DR-Mesh on weaker models such as the R-Mesh and the LR-Mesh.
@article{2005_ijfcs, author = {Fern\'andez-Zepeda, Jos\'e Alberto and Fajardo-Delgado, Daniel and C\'ardenas-Haro, Jos\'e Antonio and Bourgeois, Anu G.}, title = {Efficient simulation of an acyclic directed reconfigurable model on an undirected reconfigurable model}, journal = {International Journal of Foundations of Computer Science}, volume = {16}, number = {01}, pages = {55--70}, year = {2005}, doi = {10.1142/S0129054105002863}, keywords = {Model simulation, Reconfigurable computing, Directed models, Reconfigurable bus-based models}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
2004
- ipdps
 Efficient simulation of the acyclic DR-Mesh on the LR-MeshJ. A. Fernandez-Zepeda, D. Fajardo-Delgado, J. A. Cardenas-Haro, and A. G. BourgeoisIn 18th International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, 2004. Proceedings. , Apr 2004
Efficient simulation of the acyclic DR-Mesh on the LR-MeshJ. A. Fernandez-Zepeda, D. Fajardo-Delgado, J. A. Cardenas-Haro, and A. G. BourgeoisIn 18th International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, 2004. Proceedings. , Apr 2004Summary form only given. We present a simulation of an acyclic n/spl times/n DR-Mesh on an n/spl times/n LR-Mesh. The simulation is efficient in regards to size since both models use the same number of processors. The worst execution time for this simulation is O(n/sup 2/) time, but we demonstrate that its average execution time is O(log n). The existing fastest simulation takes O(log n) time, but it uses an extremely large number of processors. On the other hand, the most efficient simulation in terms of size takes O(log/sup 2/ n) time with O(n/sup 4//log/sup 2/ n) processors. Both of the existing simulations are for the unrestricted DR-Mesh. This paper provides an important step to efficiently simulate the unrestricted DR-Mesh on weaker models such as the R-Mesh and the LR-Mesh.
@inproceedings{2004_ipdps, author = {Fernandez-Zepeda, J. A. and Fajardo-Delgado, D. and Cardenas-Haro, J. A. and Bourgeois, A. G.}, booktitle = {18th International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, 2004. Proceedings.}, title = {Efficient simulation of the acyclic DR-Mesh on the LR-Mesh}, year = {2004}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {173--178}, keywords = {computational complexity, digital simulation,parallel processing, grid computing, acyclic DR-Mesh simulation, LR-Mesh;computational complexity, Computational modeling}, doi = {10.1109/IPDPS.2004.1303175}, issn = {}, isbn = {0-7695-2132-0}, month = apr, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {TngB4hIAAAAJ}, }
